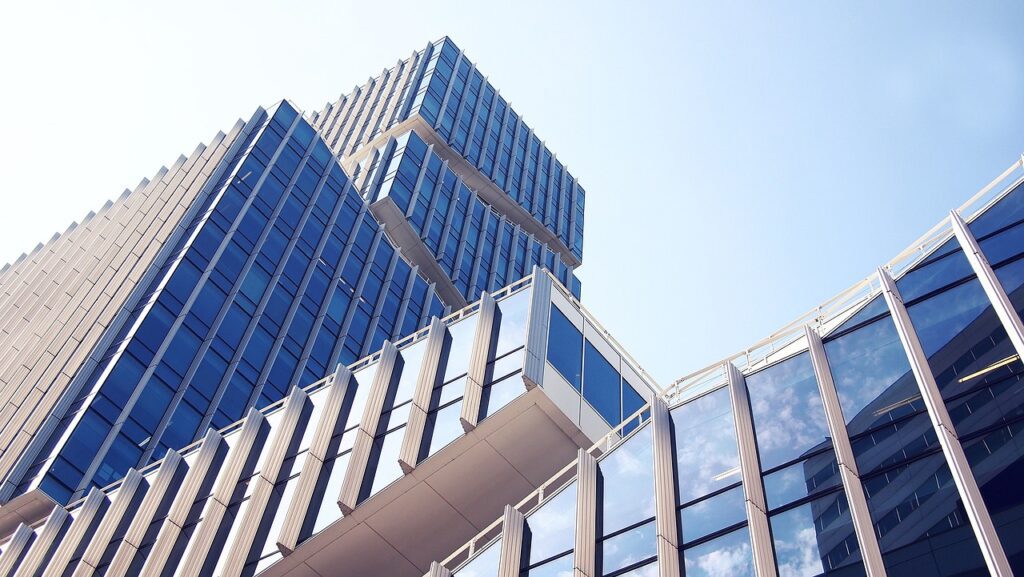
Commercial leasing in Australia involves various legal and financial aspects that both tenants and landlords must understand. This article will explore the essential factors that Australian tenants and landlords should consider during the commercial leasing process.
For Tenants
Lease Terms: Ensure you understand the lease duration, rent amount, rent review mechanisms (e.g., fixed or CPI increases), and any additional fees or charges. Familiarise yourself with your obligations and the consequences of defaulting on the lease.
Exclusive Use and Permitted Use Clauses: Verify that your business has exclusive rights to operate within the premises or building, particularly in competitive industries or when offering unique services. Understand the permitted use of the premises, as this can impact your ability to conduct your business operations.
Outgoings: Establish which outgoings (e.g., council rates, water rates, insurance, and property management fees) you are responsible for paying and whether these costs are included in the rent or paid separately.
Maintenance and Repair Responsibilities: Determine who is responsible for maintaining and repairing the property, including structural components, electrical systems, plumbing, and heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems.
Insurance: Confirm that the landlord has adequate insurance coverage for the property and consider obtaining your own insurance to cover any potential losses or damages to your business.
Termination and Renewal Options: Review the lease’s provisions for termination and renewal, including any notice requirements and conditions for renewal.
For Landlords
Creditworthiness of Tenants: Verify the creditworthiness of potential tenants by conducting credit checks and referencing previous landlords or business associates.
Rent Collection: Establish a clear and consistent rent collection process, including due dates, payment methods, and consequences for late payments or non-payment.
Compliance with Laws and Regulations: Ensure that your property complies with all applicable laws and regulations, including zoning laws, building codes, and accessibility requirements.
Subletting and Assignment: Specify whether tenants are permitted to sublet or assign their lease to another party and, if so, establish clear guidelines and approval processes.
Default and Remedies: Outline the consequences of default, including the landlord’s remedies for non-payment of rent or other breaches of the lease agreement.
Lease Regi stration:Depending on the lease term, you may need to register the lease in your state or territory, which can provide additional security for both parties.
In conclusion, commercial leasing in Australia requires a thorough understanding of the legal and financial implications for both tenants and landlords. By addressing these key considerations, you can ensure that your interests are protected and that your commercial lease aligns with your business goals and expectations.